Separator Sheet DXF
Custom separator sheets can be imported from DXF or GEO files. These sheets are typically placed between layers of a part being deposited on a bending cell, and this page explains how to set up and use a separator sheet in a deposit. The DXF should be drawn in mm, and should contain:
-
A single outer contour (closed polyline) defining the outer shape of the separator.
-
Zero or more inner contours representing the holes or cutouts in the separator sheet.
-
A few text entries of the form
Key = Valuethat define some essential properties of the separator sheet.
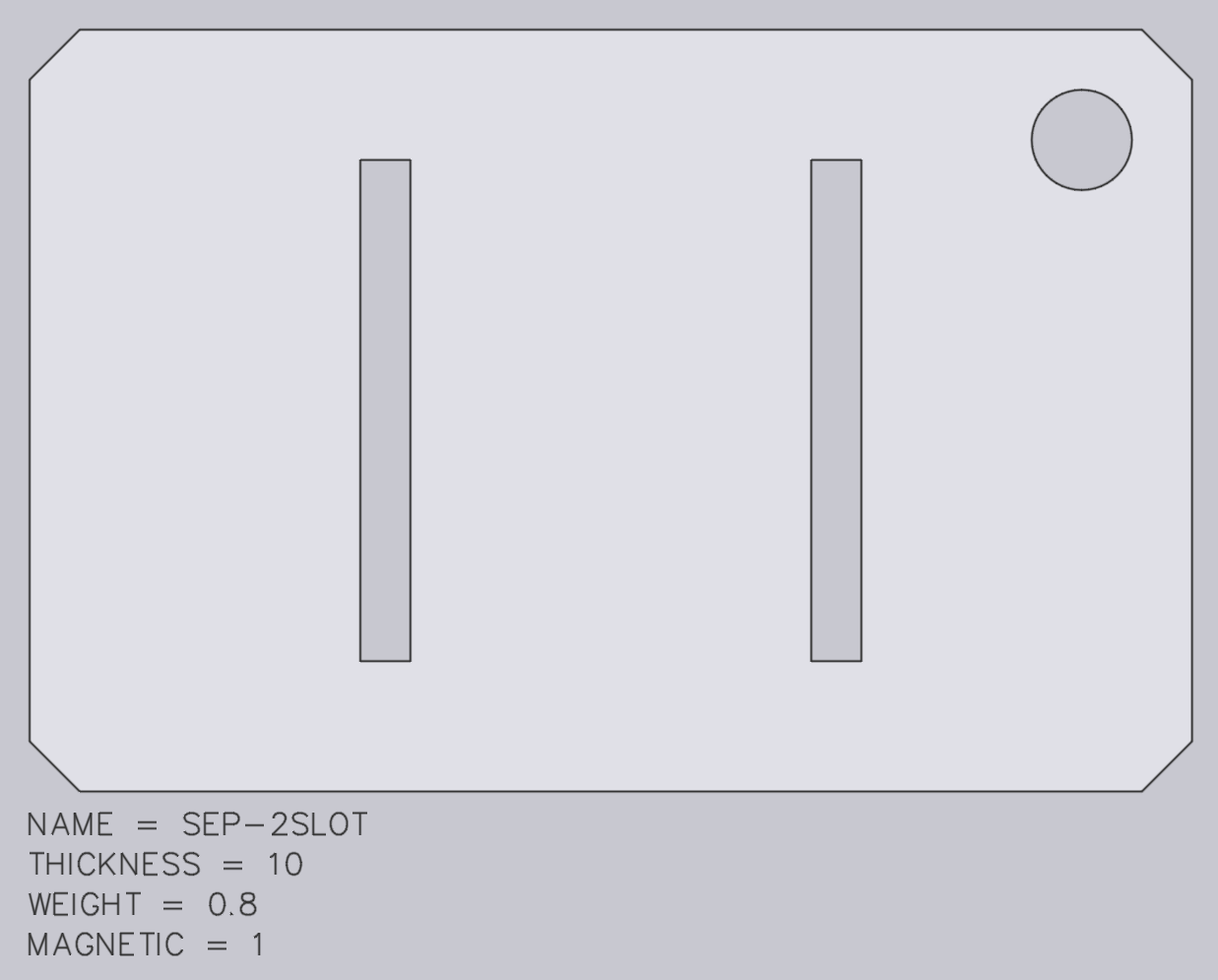
The image above shows a typical separator-sheet DXF. The exact position of the outer contour is not critical - Flux will automatically set the reference position of the separator sheet at the center of the drawing.
These keys are used to define the important metadata about the separator sheet:
-
The Name setting defines the name of the sheet (as it appears in the Flux user interface). If there is already a sheet with the same name in the separator-sheet database, it will be overwritten.
-
The Thickness is the thickness of each sheet in mm. This is an important value, since it is used to set up the correct spacing of parts on the deposit stack.
-
The Weight setting, in kg, is used to check that the gripper is not overloaded when trying to pick up the separator sheet.
-
The Magnetic setting indicates if the separator sheet is made of a ferrous material, and is used to check whether it can be picked up by a magnetic gripper. This can be omitted, and defaults to 0 (non-magnetic), which is typical for most separator sheet.